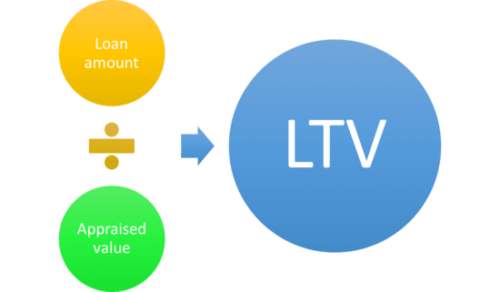
Definition of loan-to-value ratio (LTV ratio)
Your LTV Ratio is a comparison between the value of your loan and the value of your home. To determine your LTV, your lender will divide your loan amount by the lesser of the home’s appraised value or purchase price (if applicable).
Why your LTV Ratio is important
Lenders will evaluate your loan-to-value ratio while they are underwriting your loan. In general, borrowers with lower LTV ratios will qualify for lower mortgage rates than borrowers with higher LTV ratios. Borrowers who have a lower LTV ratio are considered less risky to lenders because they have more equity in their homes. In the eyes of a lender, borrowers with a lower LTV, and thus more equity in their homes, are less likely to default on their mortgage, and even if they did default, the lender would have a better chance of selling the home in foreclosure for at least as much as they are owed for the mortgage.
Other Useful Information and Links
- Qualifying for a Mortgage
- Choosing a Mortgage Lender
- Mortgage checklist
- What to ask a mortgage lender
- Mortgage Types & Rates
- Private Mortgage Insurance
- Mortgage Rates Fearbusters
- Amoritization
- Buying Vs. Renting
- Understanding Mortgage Credit Scores
- Debt to Income Ratios (what are they)
- Loan to Value Ratio
- What does a Title Co. do
- Credit Report Tips, Finding Mortgage with Bad Credit
- What is an FHA Loan?
- Bad Credit Mortgage Solutions, Fixing Credit
- Credit Scores and Reports, Mortgage Rates
- Down Payment How much do you need to save
- Mortgage Glossary
